News
-
2023/1/15
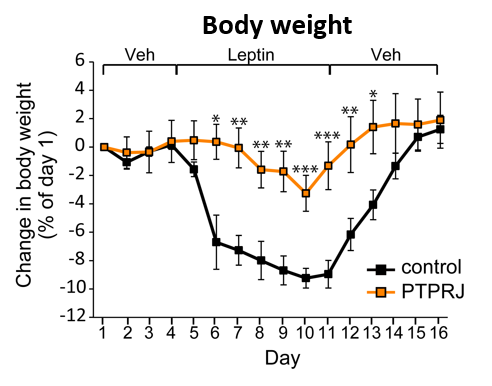
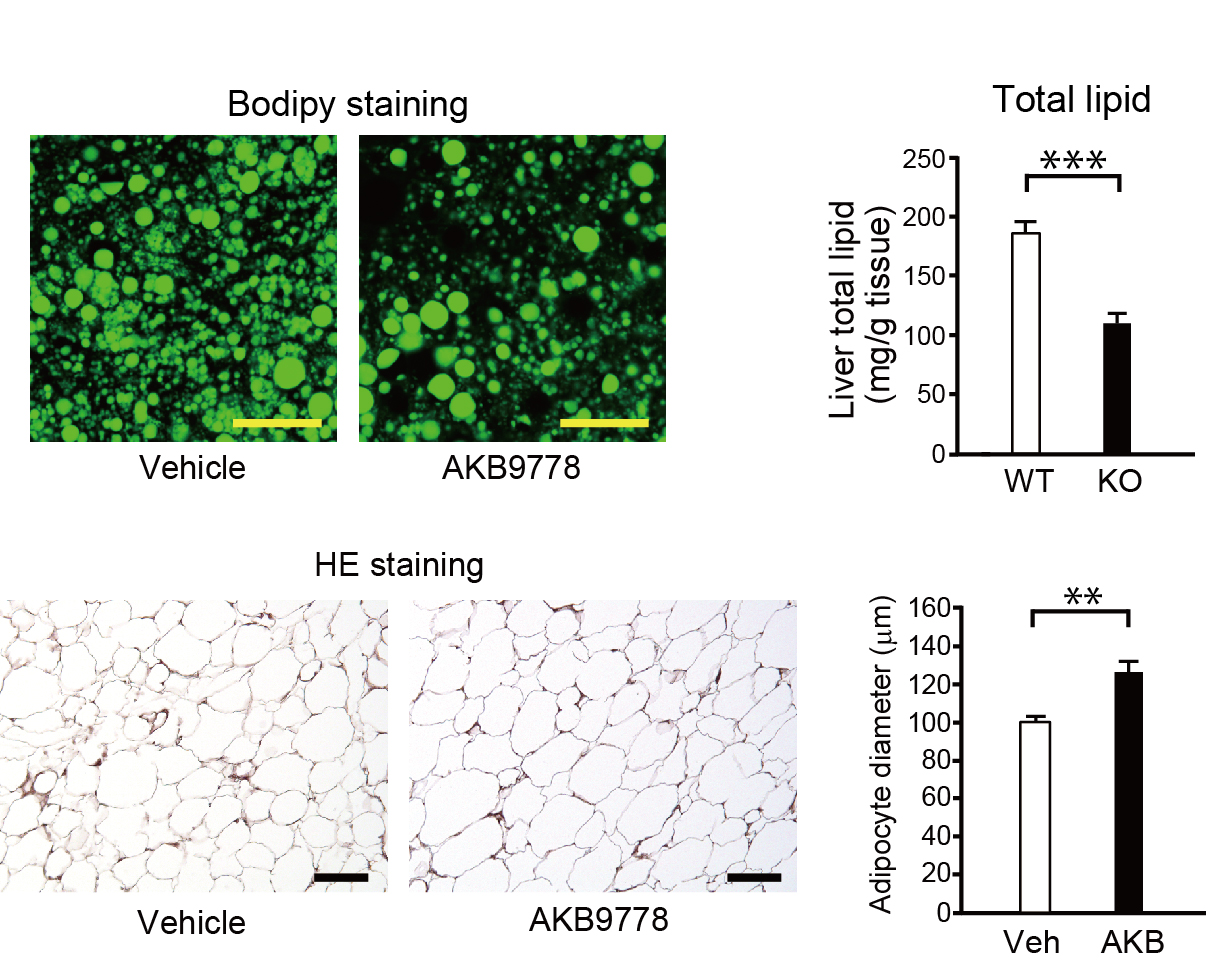
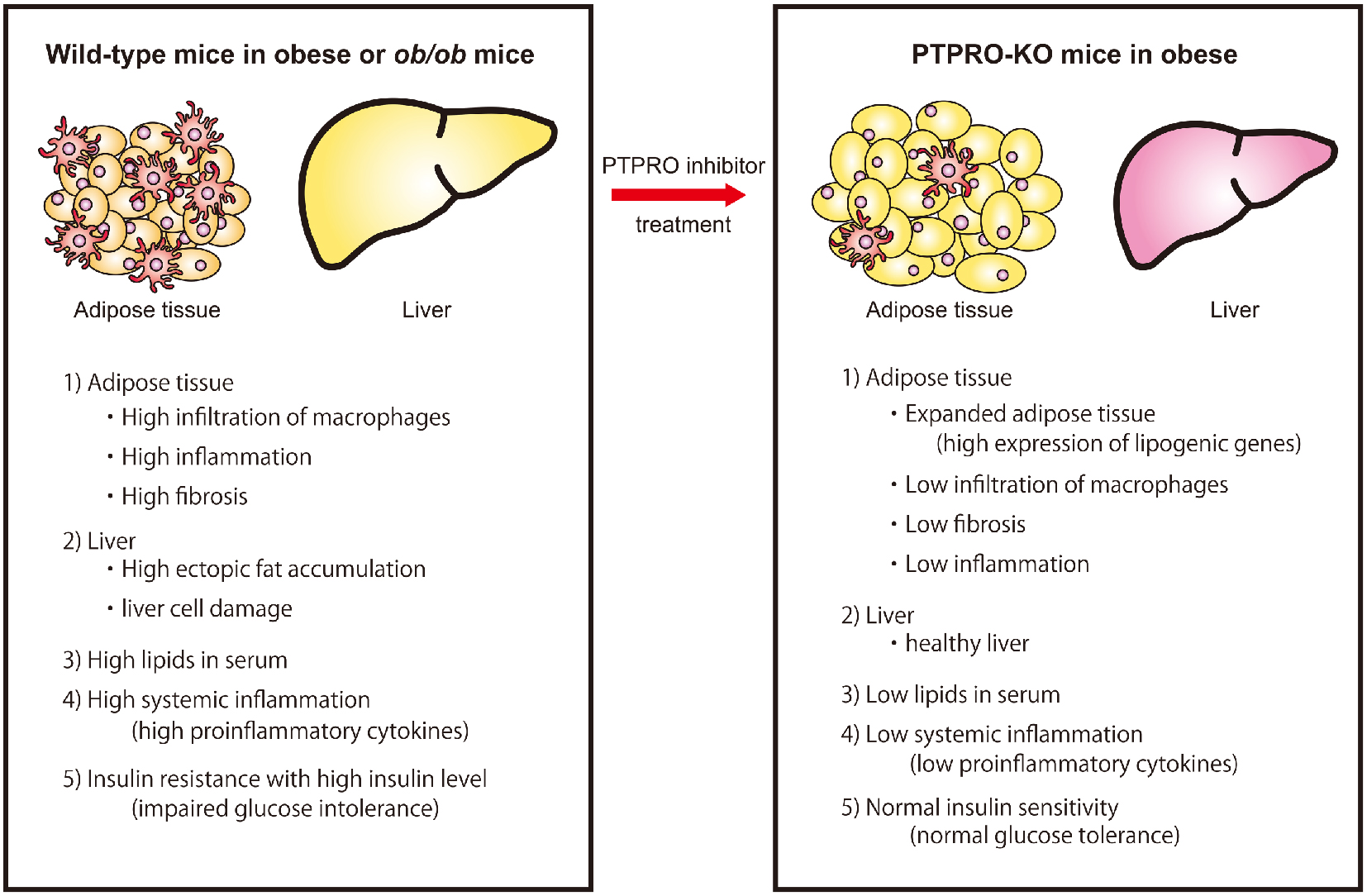
Our paper on “relationship between PTPRO activity and ectopic fat accumulation” was published in Life Sciences.
-
2022/08
Our review article on “brain mechanisms for water/salt intake control” was published in Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Ser. B, Physical and Biological Sciences.
-
2021/7/29
Professor Dr. Noda won the 23rd Toshihiko Tokizane Memorial Award.
-
2020/11/10
Our research on “water-intake control mechanisms” was published in Nature Communications.
Research
We are currently conducting research aimed at elucidating the intracerebral mechanism of fluid homeostasis and blood pressure control. We are also conducting research on obesity (metabolic control).
I
Brain mechanisms controlling blood pressure
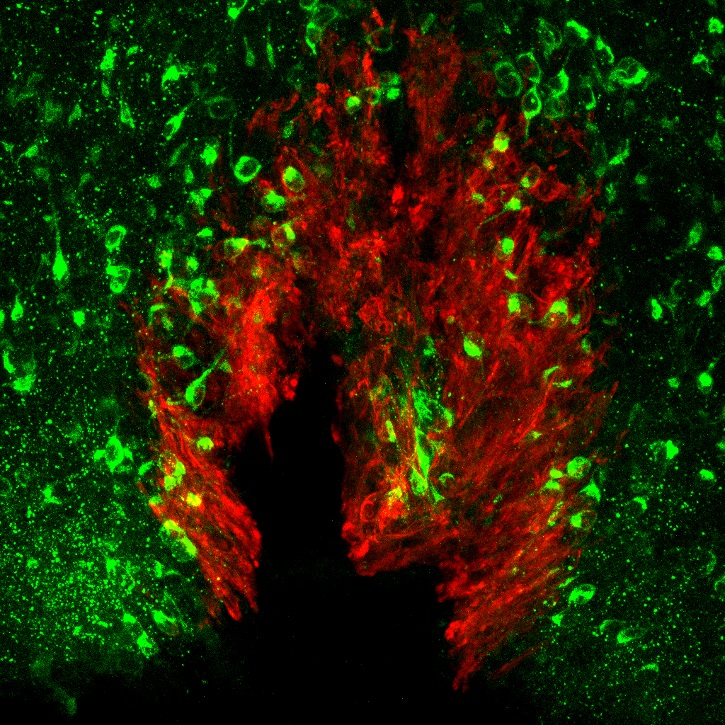
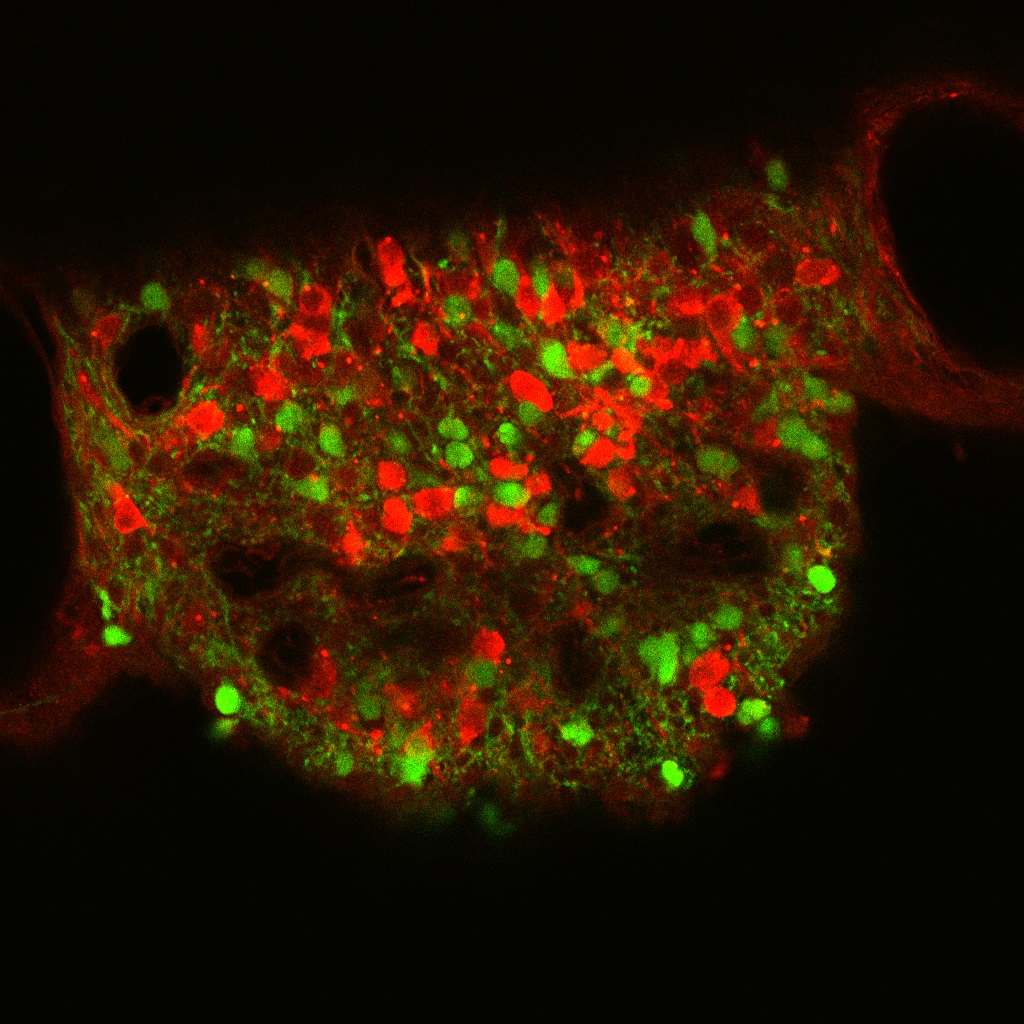
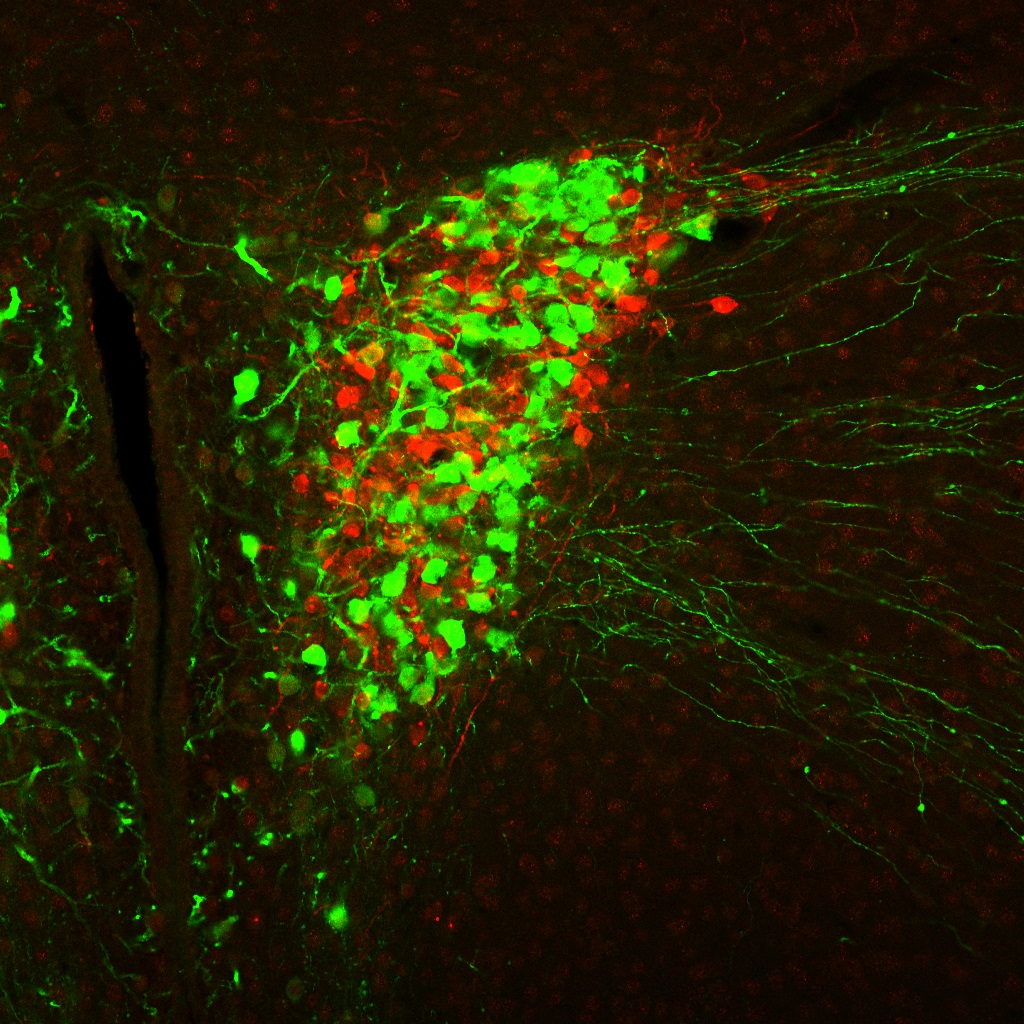
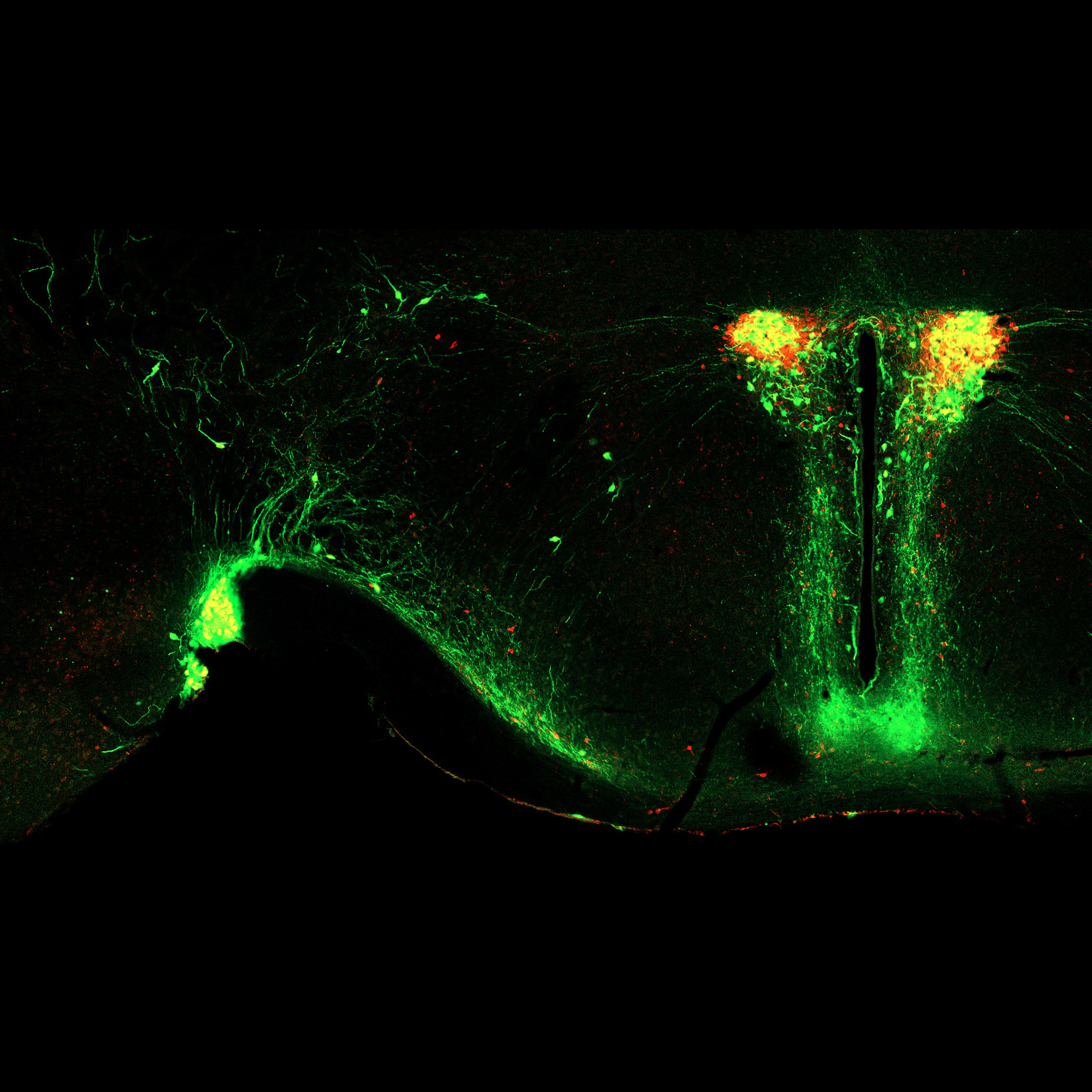
We are now promoting the study to elucidate the overall picture of brain mechanisms for ...

II
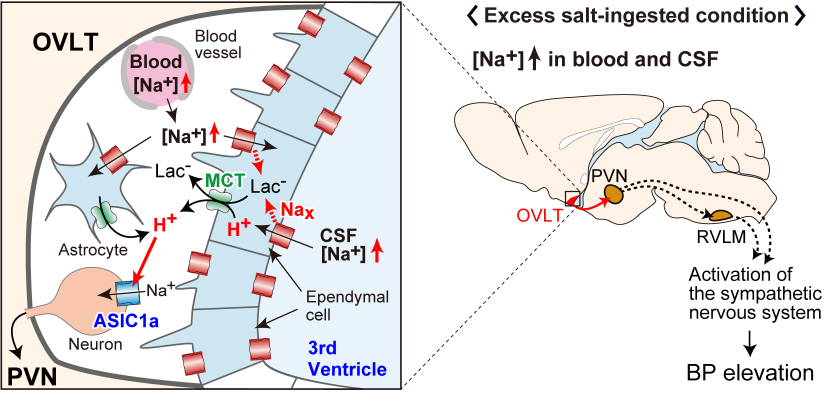
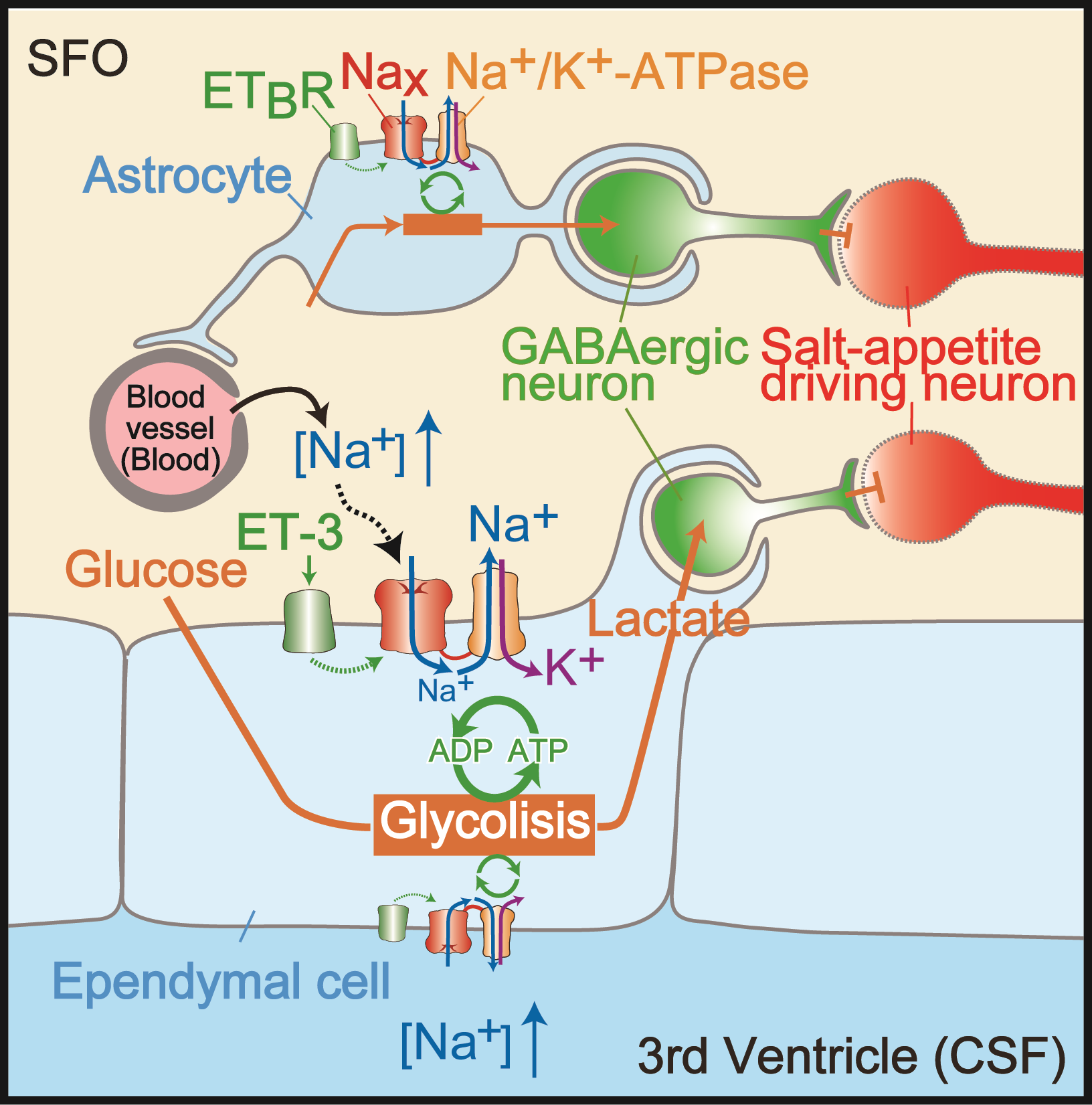
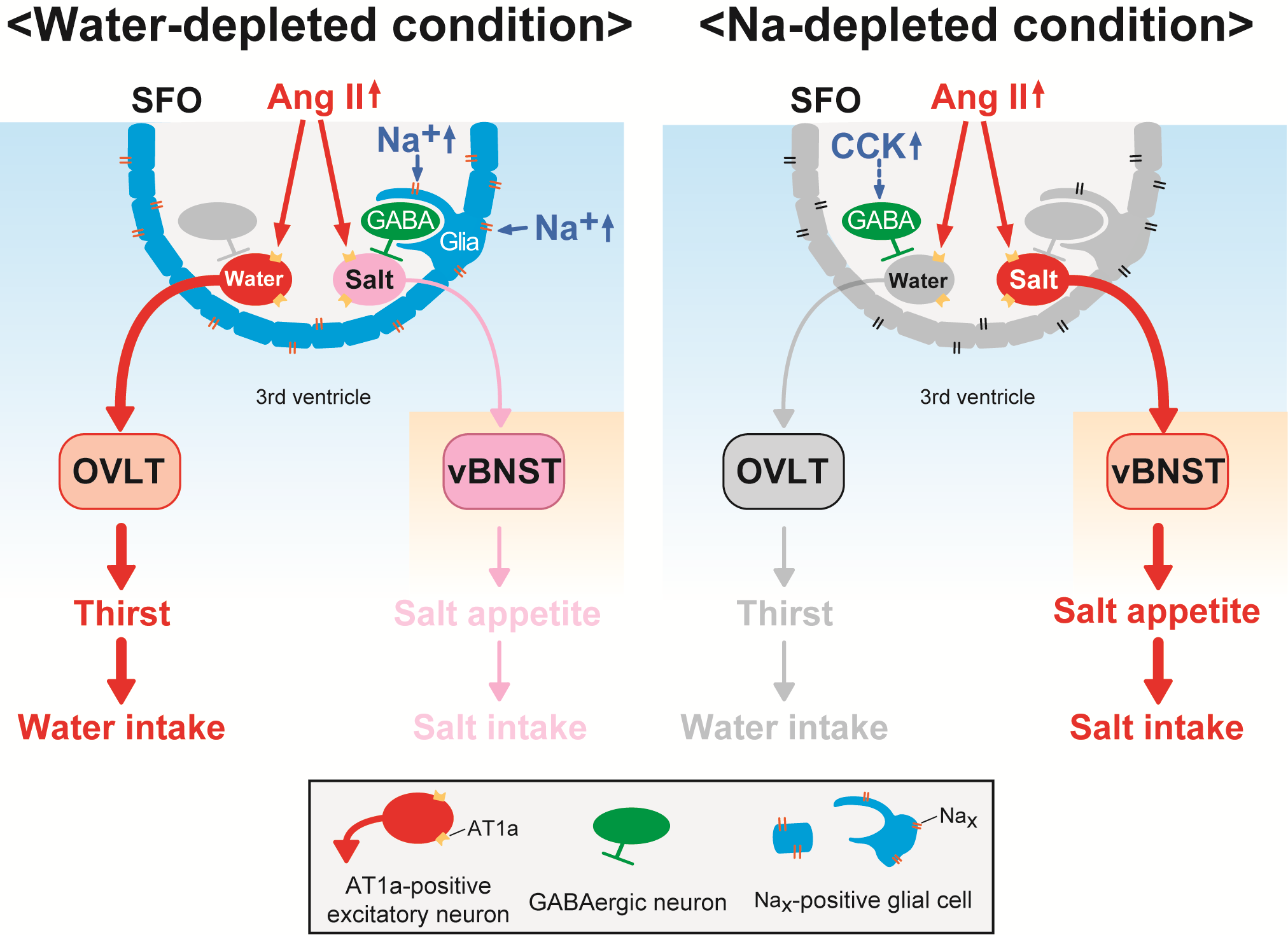
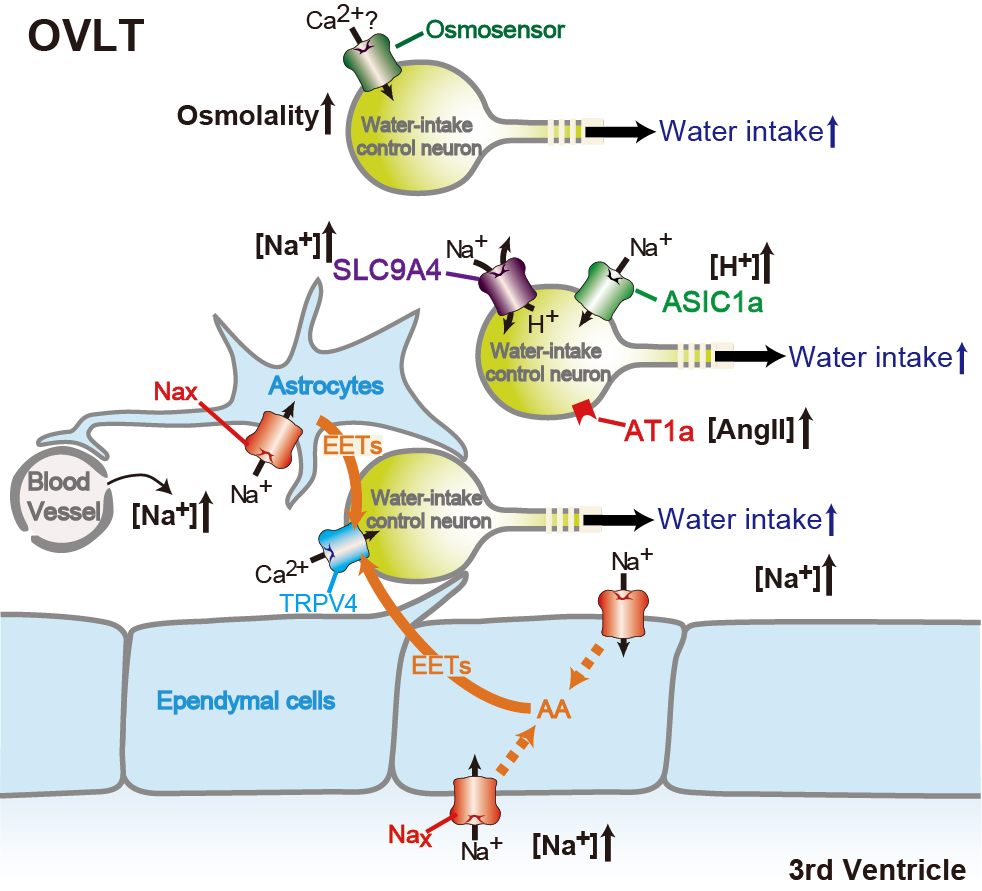
Brain mechanisms controlling thirst and salt appetite
Terrestrial animals, including humans, have mechanisms that maintain body fluid homeostasis ...
III
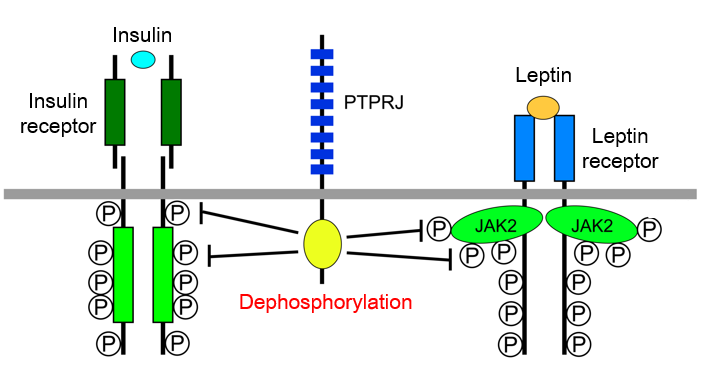
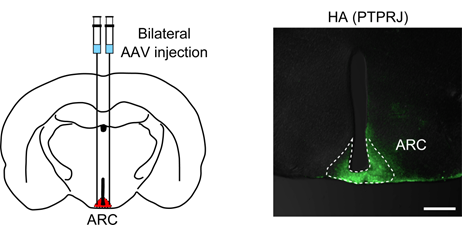
Research on obesity
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular diseases.
People

Masaharu Noda, Ph.D.
Specially Appointed Professor

Takashi Matsuda, Ph.D.
Specially Appointed Associate Professor

Keiko Ikeda, Ph.D.
Visiting Associate Professor (Lecturer)

Wu Siyuan, Ph.D.
Researcher

Yuko Kumeda.
Technical Support Staff

Mami Ishida.
Technical Support Staff

Yutaka Anzai.
Technical Support Staff

Shizuka Miyahara.
Technical Support Staff

Yukari Mutou.
Technical Support Staff

Yuka Shibuya.
Technical Support Staff

Youko Onoda.
Administrative Support Staff
Publications
(Representative recent ones)
-
Nomura K, Hiyama TY, Sakuta H, Matsuda T, Lin CH, Kobayashi K, Kobayashi K, Kuwaki T, Takahashi K,
Matsui S, Noda M.
[Na+] Increases in Body Fluids Sensed by Central Nax Induce Sympathetically Mediated Blood Pressure Elevations via H+-Dependent Activation of ASIC1a.
Neuron 101:60-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.11.017. 2019. -
Matsuda T, Hiyama TY, Niimura F, Matsusaka T, Fukamizu A, Kobayashi K, Kobayashi K, Noda M.
Distinct neural mechanisms for the control of thirst and salt appetite in the subfornical organ.
Nat. Neurosci 2017, 20, 230-241. -
Hiyama TY, Watanabe E, Ono K, Inenaga K, Tamkun MM, Yoshida S, Noda M.
Nax channel involved in CNS sodium-level sensing.
Nature Neurosci. 2002, 5, 511-512.
Contact
-
Location
4259 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku,
Yokohama, Kanagawa
226-8501 Japan -
Nearest stations
Suzukakedai Campus is a 5-minute walk from Suzukakedai Station on the Tokyu Denentoshi Line. -
Mail
noda.m.19dc@m.isct.ac.jp